home > english > Technologies > Developing lenses for XR applications
Developing lenses for XR applications
What is XR?
Technologies that blend the real world with virtual realms to enable extraordinary experiences fall under the general category of extended reality/cross reality (XR) applications. Thus, XR encompasses image processing technologies such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality (VR/AR/MR).
The term XR was coined as various technologies emerged that combine VR, AR, or other elements. For example, it may be hard to define VR games played on a head-mounted display that incorporate AR content as either VR or AR technology. This is why the catch-all term XR was created.
Head-mounted displays
Those looking to experience the world of XR will need a head-mounted display (also called VR goggles) or other special equipment. These take the form of a pair of goggles, and their appeal becomes clear once they are worn: video images can be watched as if on a large screen, and one can enjoy VR games.
Head-mounted displays contain LED light sources and compact liquid crystal displays. The images on these LED-illuminated displays reach the wearer's eyes at close range.
Lenses for this arrangement are where Kantatsu development is now focused.
XR lenses from Kantatsu
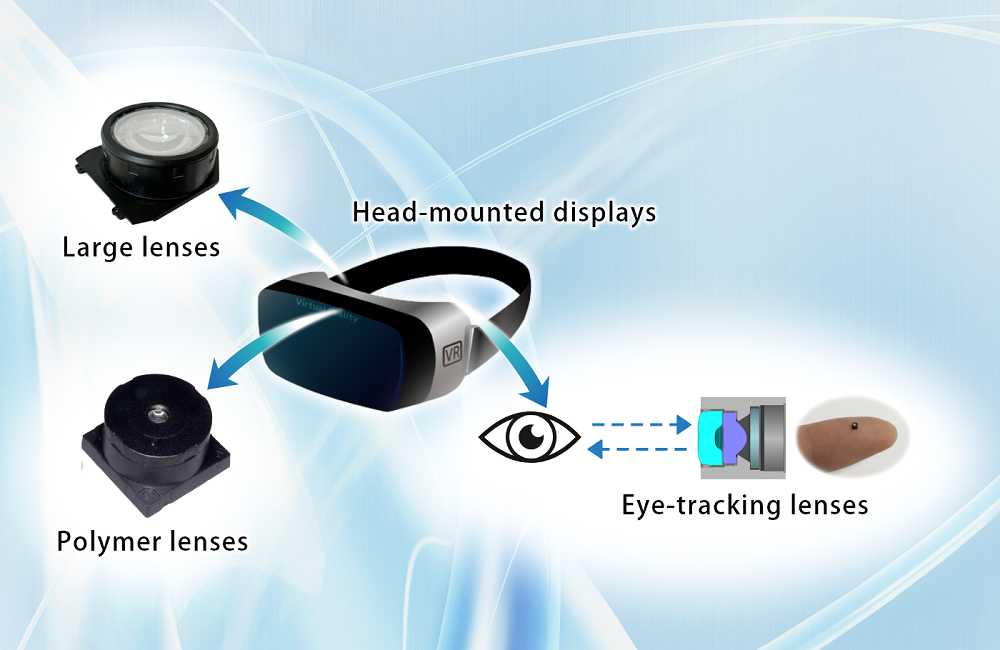
Large lenses
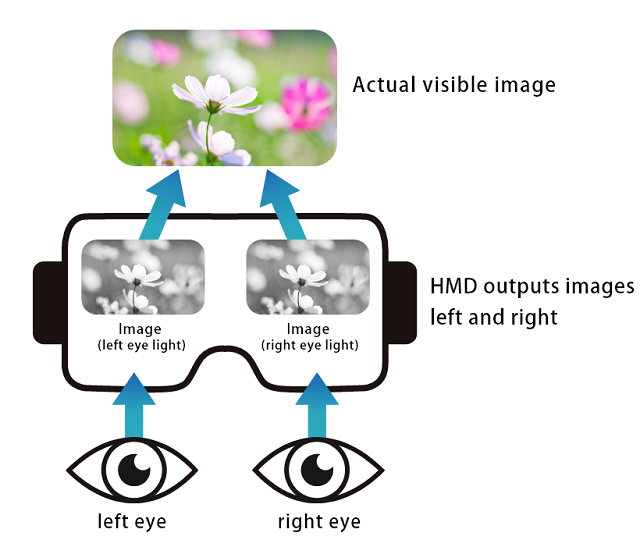
When we view the real world, our left and right eyes each give us a slightly different view. This subtle misalignment produced by our eyes helps us recognize the distance to objects, as well as their respective sizes. Head-mounted displays (HMDs) apply this principle to recreate a 3D space by displaying slightly different images for our left and right eye.
Large lenses are positioned between inner HMD displays and our eyes. HMDs incorporate two units as eyepiece lenses for retinal focusing.
With large-aperture lenses from Kantatsu, the two large lenses provide a slimmer structure, images that are brighter than competitive models while consuming less power, and image reproduction that is extremely natural, with minimal distortion or deformation. This is an advantage of high-precision Kantatsu molding and assembly technologies.
Polymer lenses
-
Polymer lenses (as used by RGB cameras1) are mounted on the front of HMDs to capture and display real-world images of one's surroundings, or to show the real-world surroundings like a window layered over a portion of the VR world.
These are ultra high-speed autofocus lenses consisting of an optical-polymer lens core and piezo actuator. To control the lens focal length, an electric voltage is applied to the actuator to deform the lens core shape. Autofocusing by conventional lenses involves a voice coil motor (VCM), which moves the lens relative to the image sensor. High-speed, high-precision movement is required so that the unit can quickly adjust and keep images in focus. This makes sharp and accurate image capture difficult. Polymer lenses can eliminate this shortcoming. These lenses simply change the shape of the element consisting of optical polymer to quickly focus on objects at different working distances or at different heights. Actual autofocusing is extremely fast, at 1 ms. This is about 10 times faster than lenses with a VCM.
What's more, unlike lenses with a VCM, polymer lenses do not alter the angle of view (the image area shown) even if the focal position moves - a great advantage in preventing an HMD issue called VR sickness. This makes polymer lenses ideal for applications that require high-speed focusing or transmission, as well as applications requiring an adjustable depth of field or working distance. -
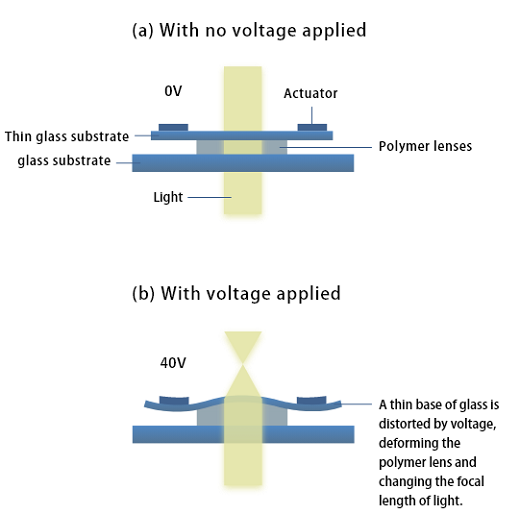
Operating image of polymer lens
In this way,Kantatsu polymer lenses provide ultra fast autofocus and low power consumption without altering the angle of view during autofocus. This is an advantage of the high-precision optical design, interlock, and assembly technologies used by Kantatsu.
1: A type of digital camera. In this system, an image sensor converts light into electrical signals that provide the image data.
Eye-tracking lenses
As the name implies, eye-tracking technology tracks and analyzes how our eyes move or where we look. This functionality allows devices to apply information about eye movement to the virtual images displayed. Thus, the line of sight of a user's avatar can be linked to their own line of sight and moved accordingly, which enables smoother communication in VR. It is a new and highly anticipated feature that will further enhance immersiveness and seamlessness in future VR content.
Eye-tracking lenses are used in the ultra compact cameras for eye detection. Their ultra compact size is essential, because multiple cameras of this kind are mounted in a limited space inside HMDs.
Kantatsu eye-tracking lenses are the world's slimmest and extremely compact, but despite their space-saving design, they also offer high resolution from superior optical characteristics. This is an advantage of the ultra compact, high-performance, high-precision optical design technology, original advanced mold technology, and high-precision molding technology for ultra compact microlenses used by Kantatsu.